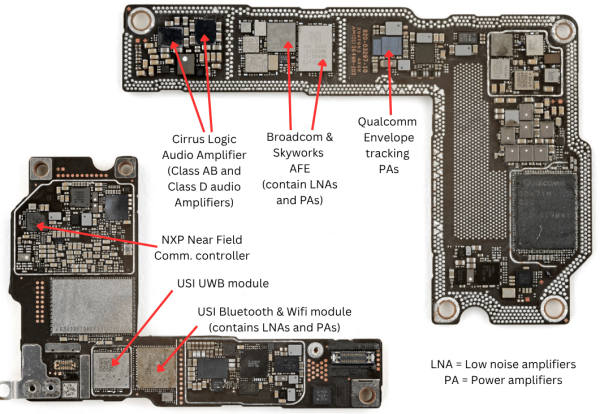
Amplifiers¶
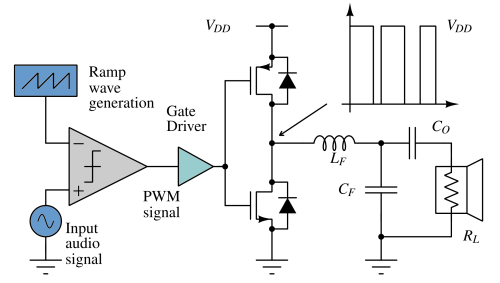
Class D amplifiers use high-speed switching and PWM to achieve high-efficiency audio amplification, ideal for compact audio systems.
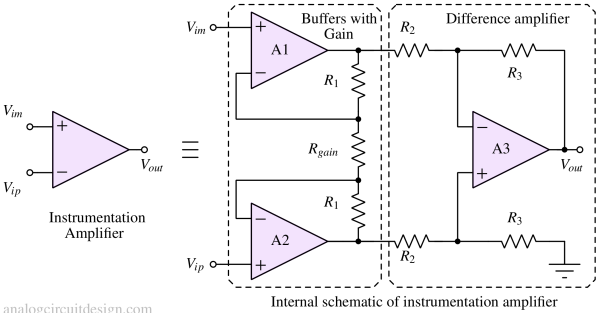
Instrumentation amplifiers are precision amplifiers designed to amplify small differential signals while rejecting common-mode noise.
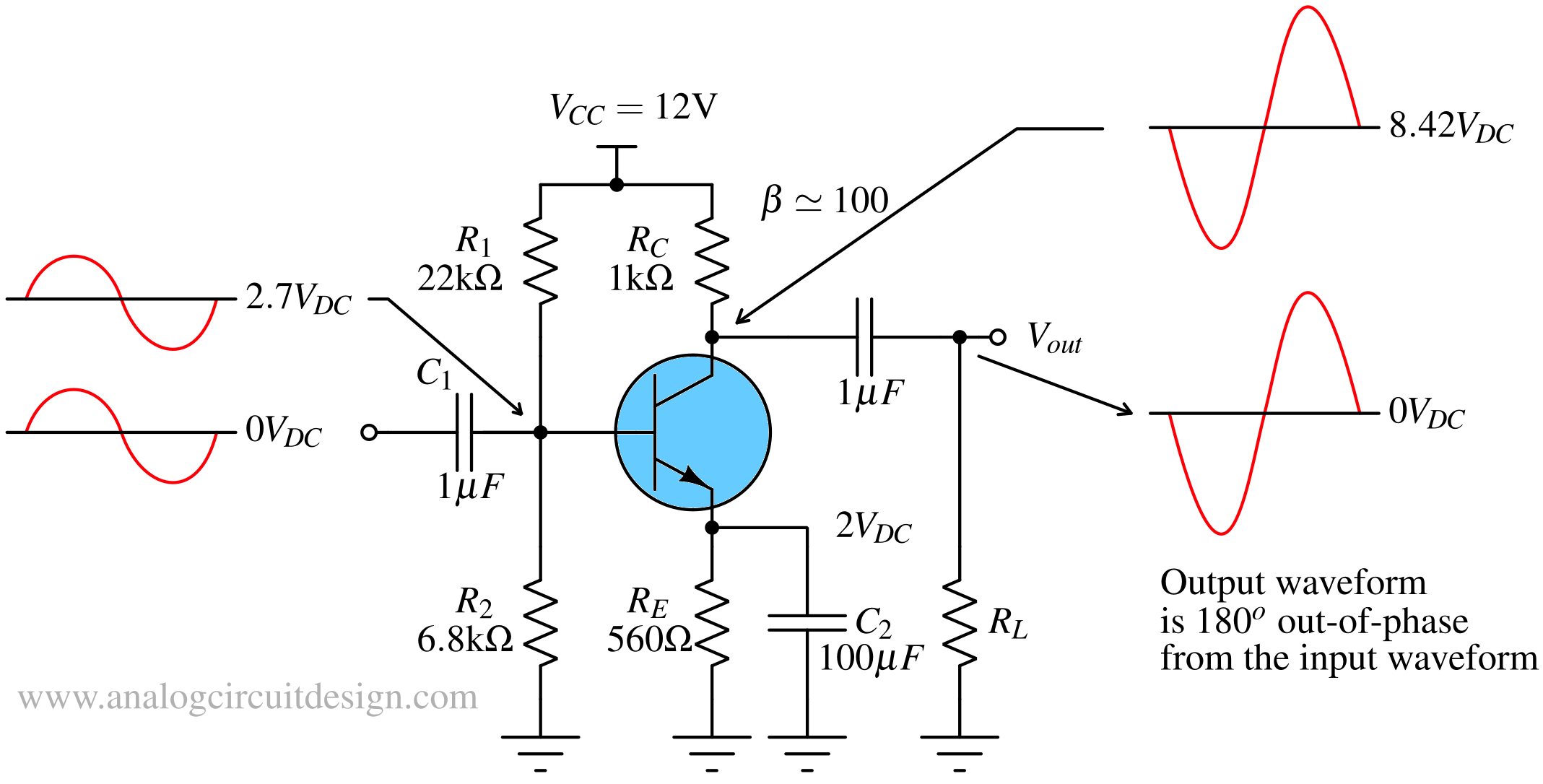
A common emitter amplifier is a BJT configuration where the emitter is shared between input and output, providing high voltage gain and phase inversion.
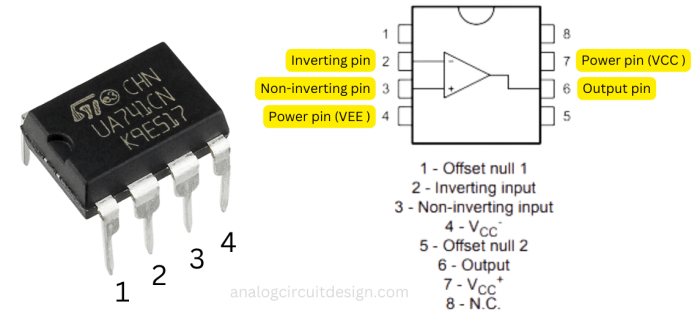
The IC 741 is a general-purpose operational amplifier with high gain, differential input, and low output impedance, widely used in analog circuits.
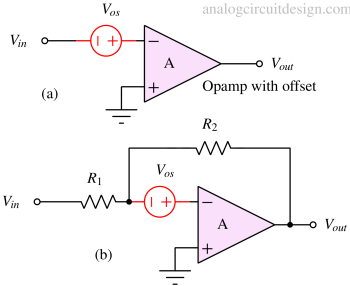
Op-amp offset voltage is the differential DC voltage required between the input terminals to make the output voltage zero.
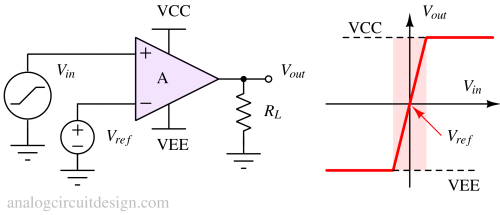
An op-amp comparator compares two input voltages and produces a digital output indicating which input is higher.

A common base amplifier is a BJT configuration where the base is the shared terminal, offering low input impedance, high output impedance, and wide bandwidth.
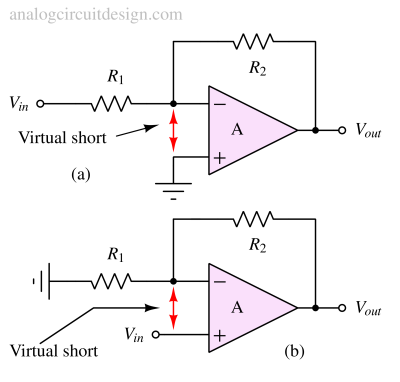
The concept of a virtual short in negative feedback op-amp circuits refers to the condition where the inverting and non-inverting inputs are at nearly the same potential without being physically connected.
Operational amplifiers (op-amps) are versatile components used in amplification, filtering, signal conditioning, and mathematical operations in electronic circuits.
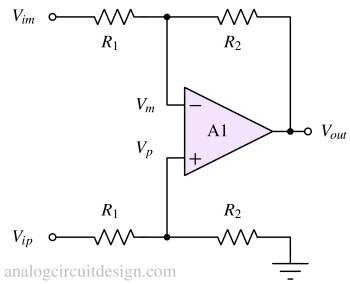
A Voltage Subtractor, often implemented as a Difference Amplifier, is an op-amp circuit that produces an output proportional to the difference between two input voltages while rejecting common-mode signals.
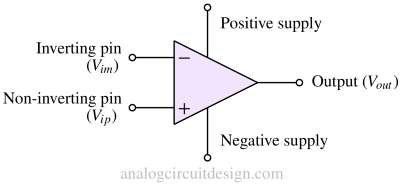
An operational amplifier (op-amp) is a high-gain voltage amplifier with differential inputs and a single-ended output, widely used in analog circuits.
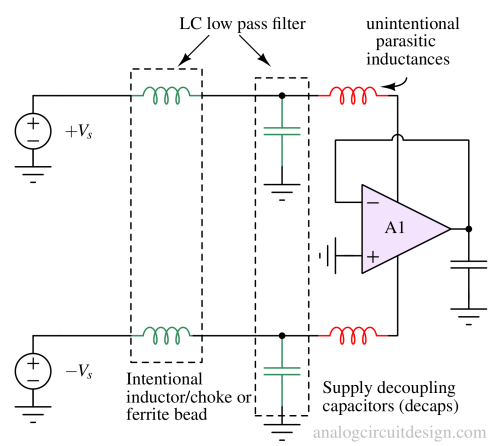
A supply bypass capacitor is connected across a power supply to filter out noise and provide a stable DC voltage to electronic circuits.
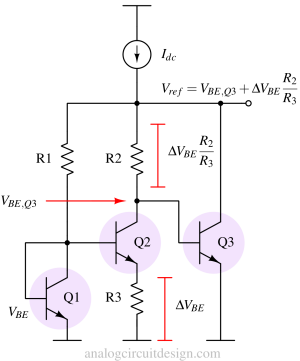
A bandgap voltage reference provides a stable, temperature-independent reference voltage, typically around 1.2 V, using semiconductor properties.
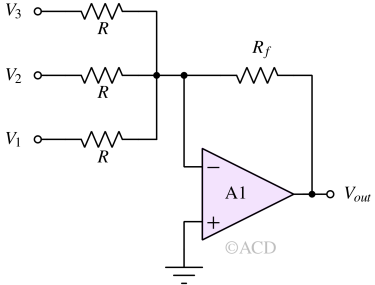
A summing op-amp produces an output voltage proportional to the weighted sum of multiple input voltages.
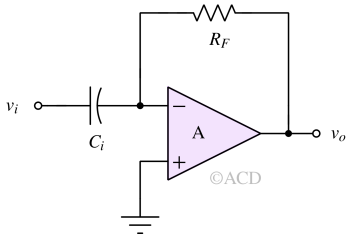
A Voltage Differentiator is an op-amp circuit that produces an output voltage proportional to the rate of change of the input signal, effectively performing the mathematical differentiation operation.
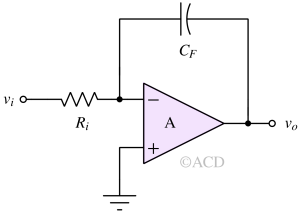
A Voltage Integrator is an op-amp circuit that generates an output voltage proportional to the time integral of the input signal, effectively performing mathematical integration.
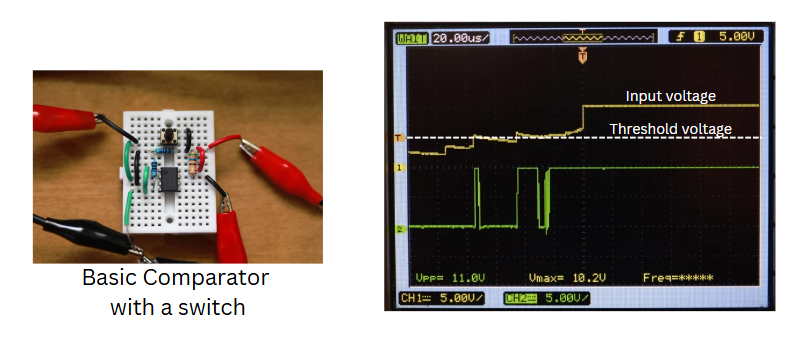
A Schmitt trigger is a comparator circuit with hysteresis that converts a noisy or analog input signal into a clean digital output.
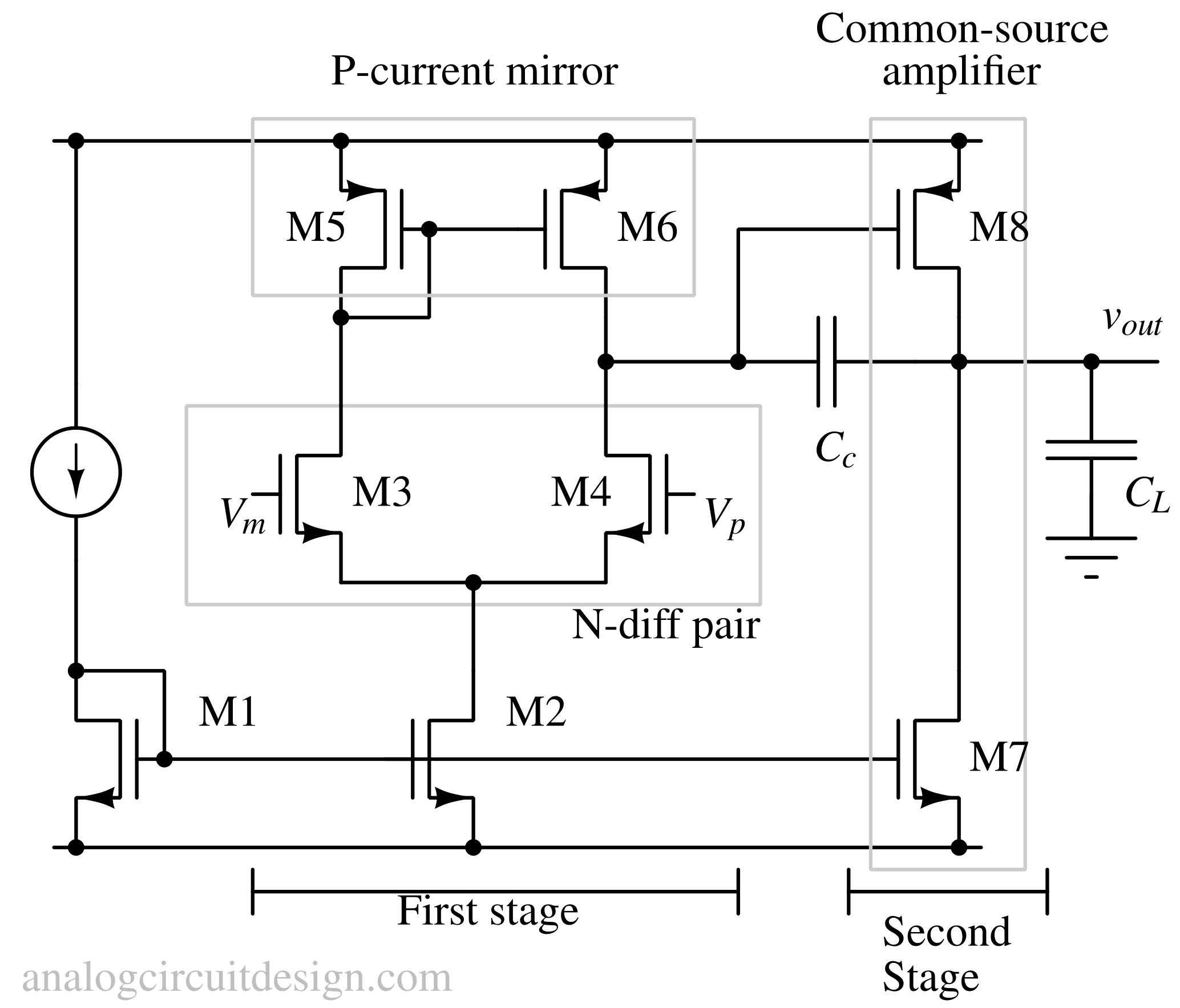
CMOS op-amps use complementary MOSFET transistors, offering low power consumption, high input impedance, and wide operating voltage ranges.
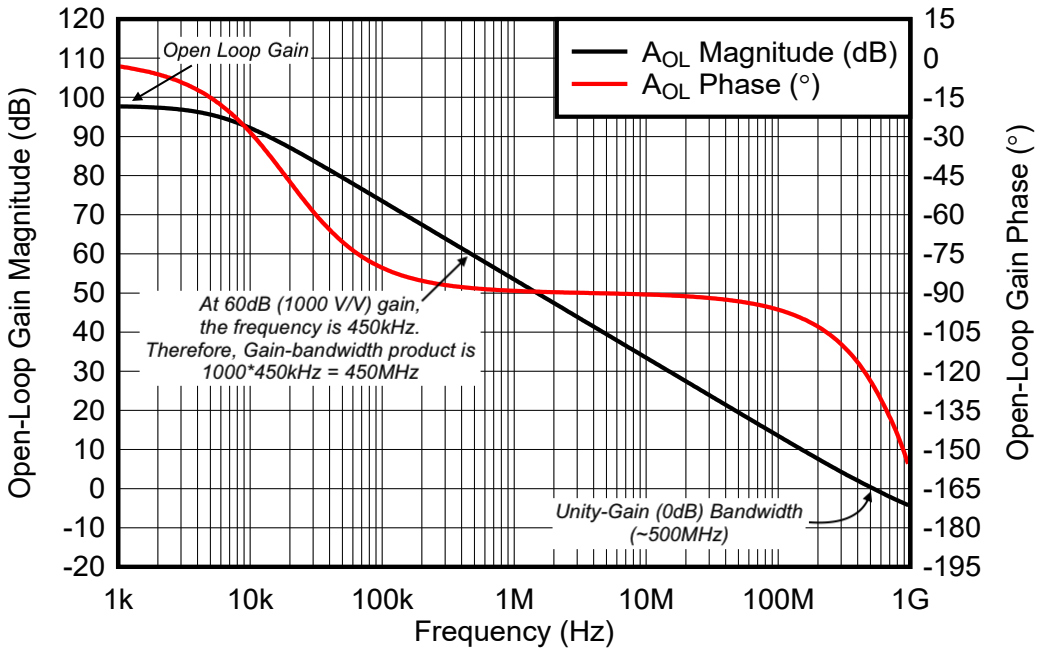
Op-amps have key properties like high input impedance, low output impedance, high gain, wide bandwidth, and differential inputs for versatile analog signal processing.
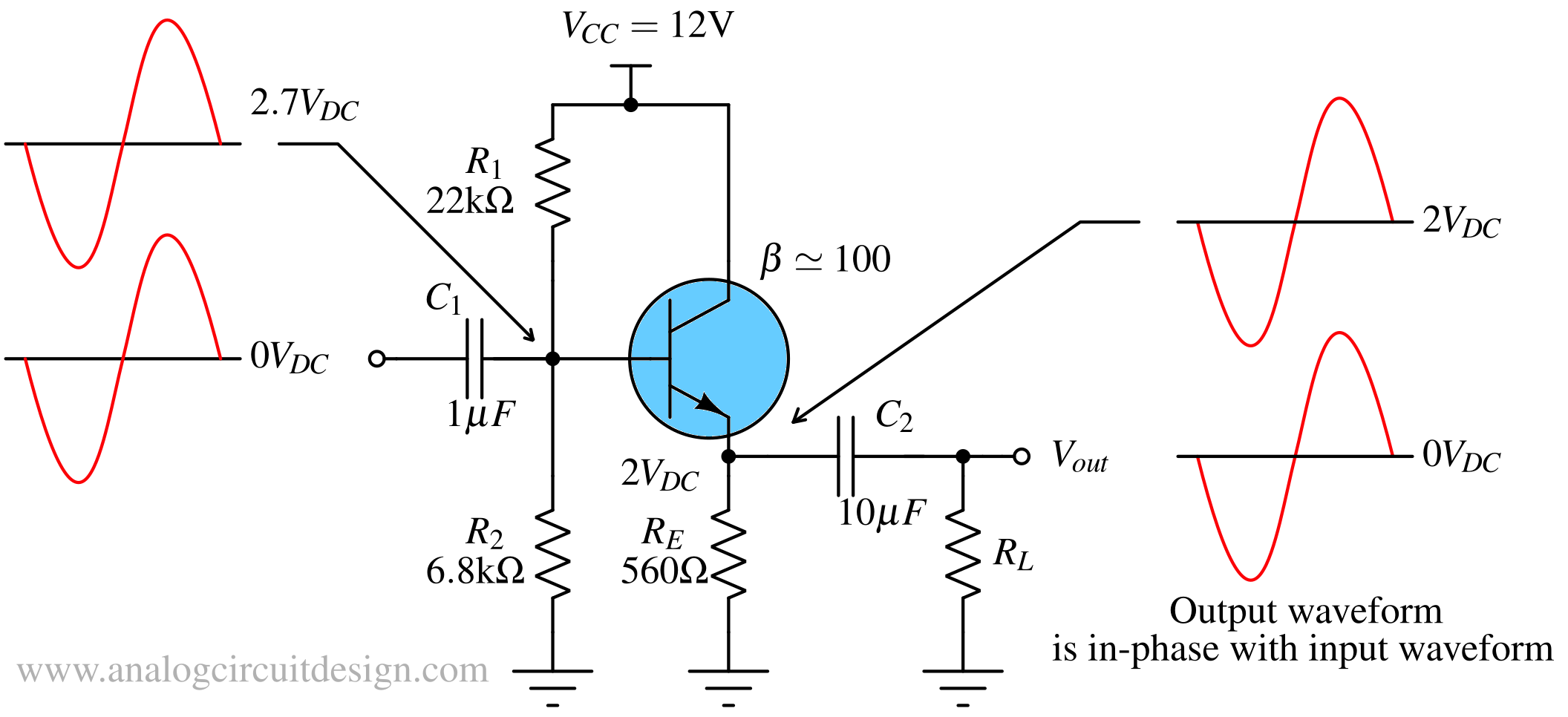
A common collector amplifier, also known as an emitter follower, provides high input impedance, low output impedance, and unity voltage gain.
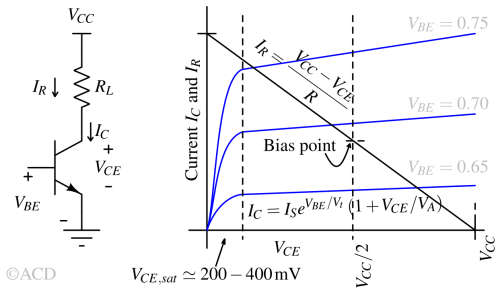
A Class A amplifier conducts output current throughout the entire input signal cycle, providing high linearity but lower efficiency due to continuous power dissipation.
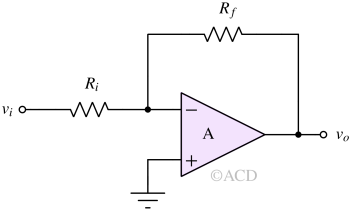
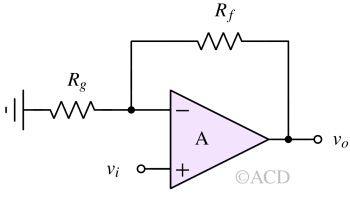
An inverting operational amplifier produces an output signal that is 180° out of phase with the input, providing controlled voltage gain.
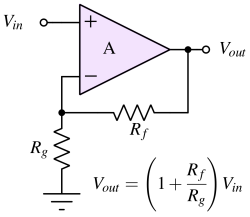
A non-inverting operational amplifier provides an output voltage that is in phase with the input voltage while offering voltage gain.