Networks¶
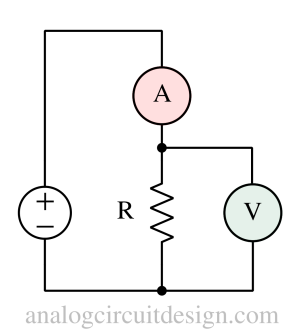
Ohm’s law states that the current flowing through a conductor is directly proportional to the voltage across it and inversely proportional to its resistance.
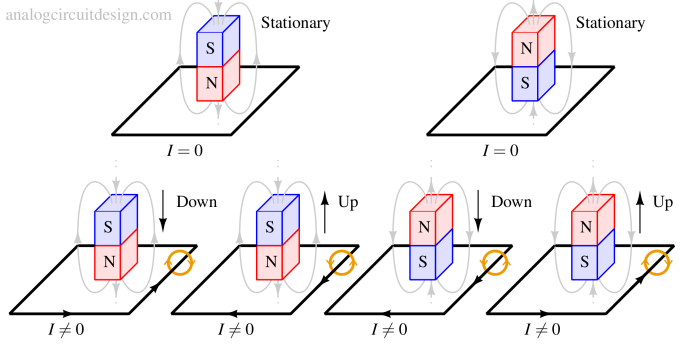
Lenz’s law states that the direction of induced current in a conductor opposes the change in magnetic flux that produced it.
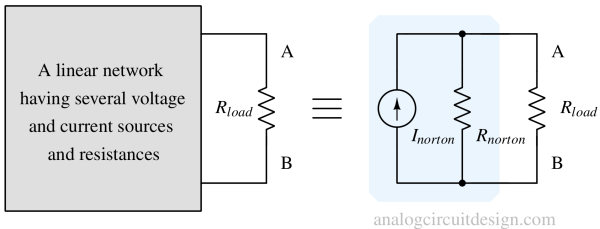
Norton’s theorem states that any linear electrical network can be replaced by an equivalent current source in parallel with a resistor.
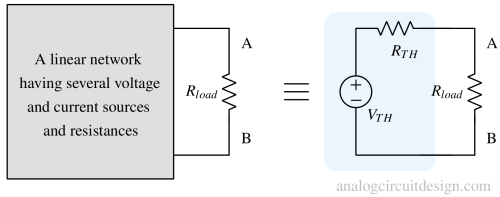
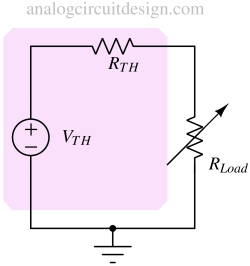
Thevenin’s theorem states that any linear electrical network can be replaced by an equivalent voltage source in series with a resistor.
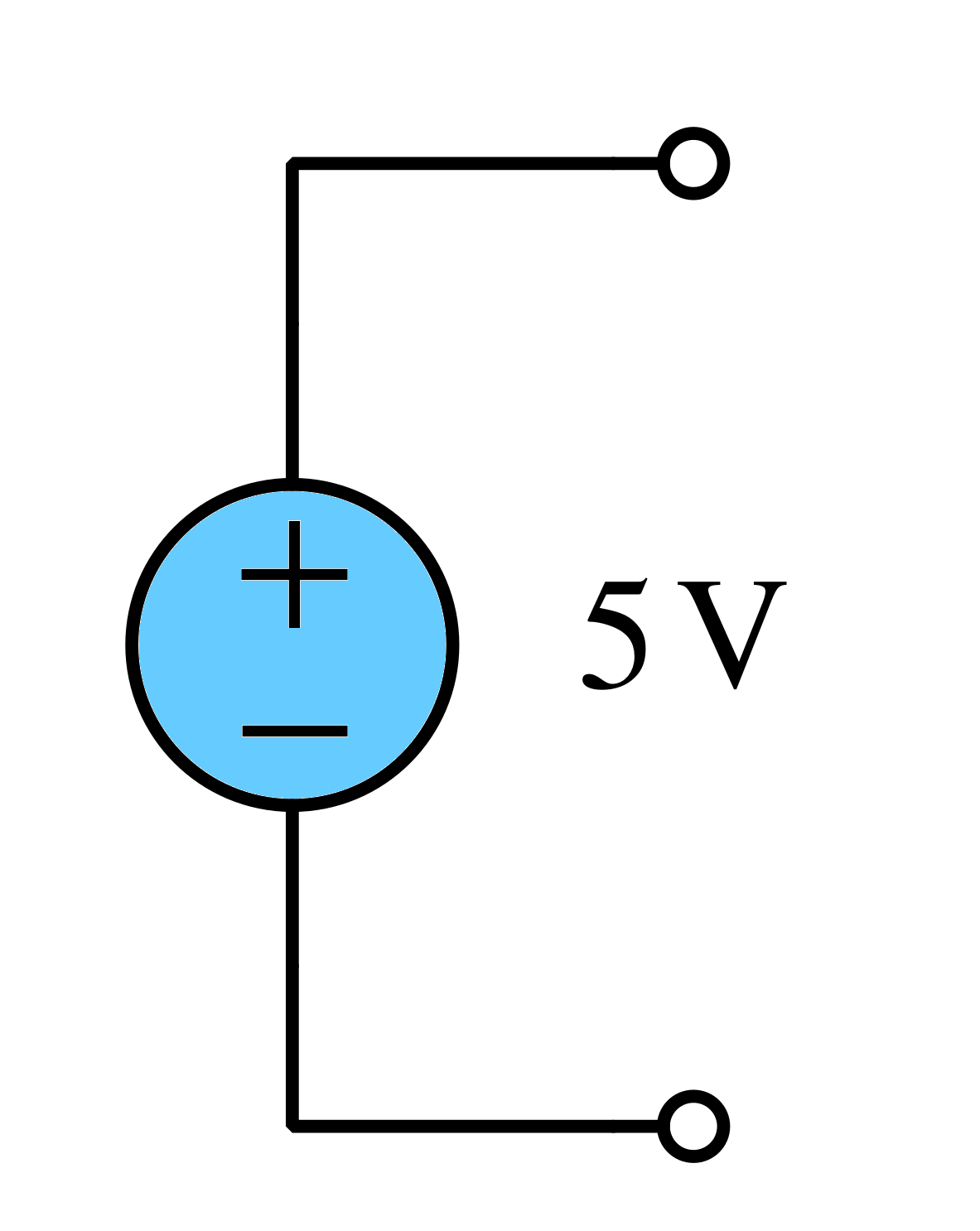
Independent sources provide a fixed voltage or current regardless of circuit conditions, while dependent sources generate voltage or current based on another voltage or current in the circuit.
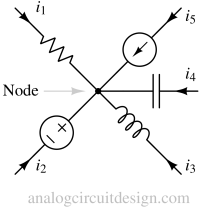
Kirchhoff’s circuit laws include the current law (KCL) and voltage law (KVL), which describe the conservation of charge and energy in electrical circuits.
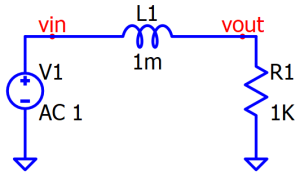
An RL circuit consists of a resistor and an inductor connected in series or parallel, used to control current and filter signals in AC and DC circuits.
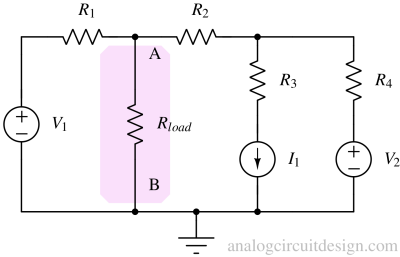
The superposition theorem states that in a linear circuit with multiple independent sources, the response in any element is the sum of the responses due to each source acting alone.
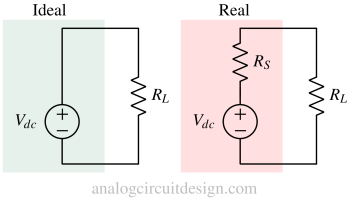
An ideal voltage source provides a constant voltage regardless of the load, while a real voltage source has internal resistance that affects the output under load.
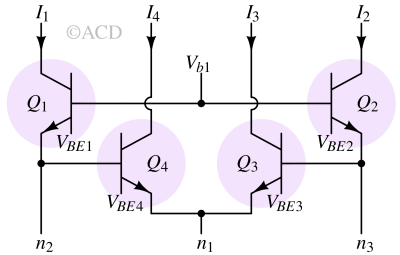
The translinear principle states that in a closed loop of bipolar junction transistors, the product of currents in one direction equals the product of currents in the opposite direction.
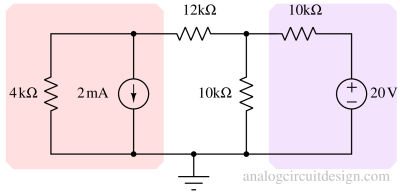
Source Transformation is a circuit analysis technique that allows the conversion of a voltage source in series with a resistor into an equivalent current source in parallel with the same resistor, and vice versa.
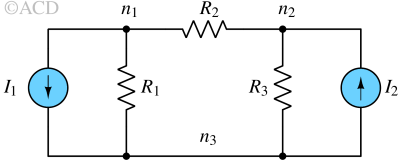
Nodal analysis is a method used to determine the voltages at different nodes in an electrical circuit using Kirchhoff’s current law.
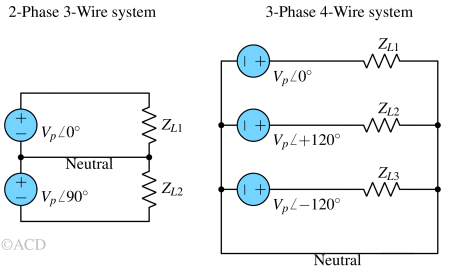
Star-Delta connection is a method of connecting three-phase windings in star (Y) and delta (Δ) configurations to control voltage and current in motors and transformers.
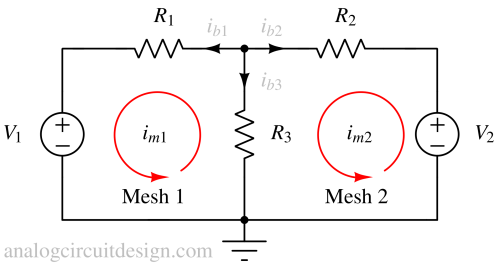
Mesh analysis is a method used to determine the currents flowing in a planar circuit by applying Kirchhoff’s voltage law to independent loops.

An RC circuit consists of a resistor and a capacitor connected in series or parallel, used to filter signals and control timing.
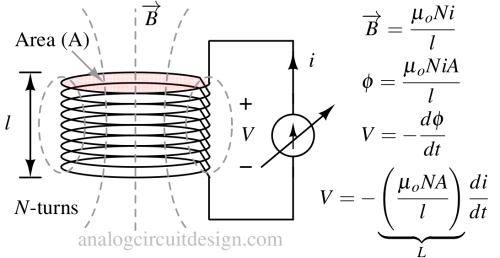
Self-inductance is the property of a coil to oppose changes in its own current, while mutual inductance is the ability of one coil to induce voltage in another nearby coil.
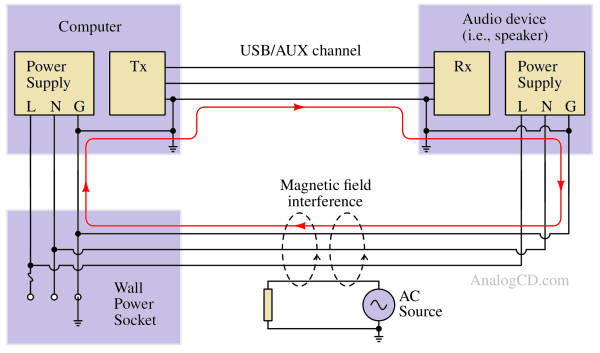
Galvanic Isolation is a technique used to separate electrical circuits to prevent direct current flow while still allowing signal or power transfer.
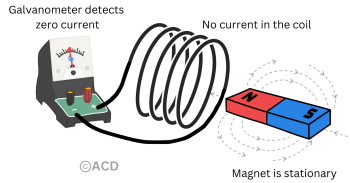
Faraday’s law of induction states that a changing magnetic field through a circuit induces an electromotive force (EMF) proportional to the rate of change of the magnetic flux.